The “Tsar Bomba” or “Product B” was created with the scope and monumentalism characteristic of the USSR. When the first project was completed, scientists and politicians were frightened of their offspring, therefore they reduced the initial power of the bomb by half. And modern Russian “hot heads” are still trying to scare the States with it.
“Tsar Bombu”, contrary to popular myth, created 7 years, not 112 days. At the height of the Cold War, in 1954, Khrushchev and Kurchatov conceived to create a weapon that would show all the possibilities of an atomic explosion. Using their advanced and American developments, the scientists wrote a draft of a 101.5 megaton bomb. For comparison, the bomb dropped on Nagasaki, had a capacity of 0.018 megatons, and the most powerful American development at that time - 15 megatons.
But such power frightened scientists. They suggested that an uncontrolled thermonuclear reaction in the atmosphere could begin, and the level of radiation contamination would be catastrophic. Therefore, more sensible minds have achieved a reduction in design capacity of up to 50 megatons - more than doubled.
Comparing the power of the Tsar Bomb with other warheads created
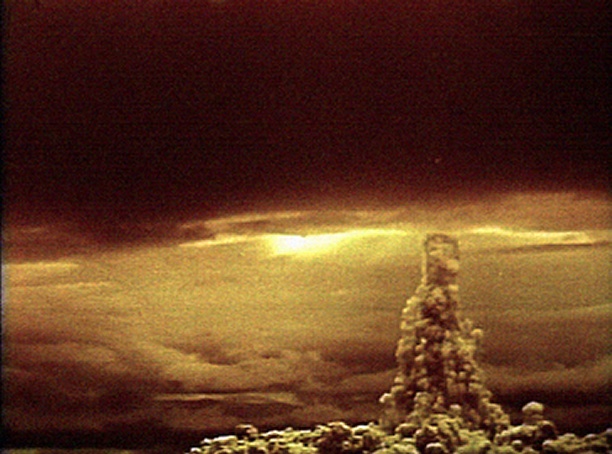
The “Product B” test took place on October 30, 1961. The carrier aircraft raised the bomb to a height of 10.5 km and dropped it on a parachute. Having managed to fly off to 39.5 km, the pilot strongly felt the force of the explosion: the plane lost 800 m in height and could hardly regain control. The power of the explosion was greater than the design and reached 58 megatons.The explosion was of such strength that the resulting seismic wave circled around the Earth three times, people felt thousands of kilometers away, and the sound was heard 800 km from the site of the explosion. Interference in radio communications lasted 40 minutes, and radiation could cause 3 degree burns within a radius of 100 km. The mushroom cloud itself reached an altitude of 67 km.

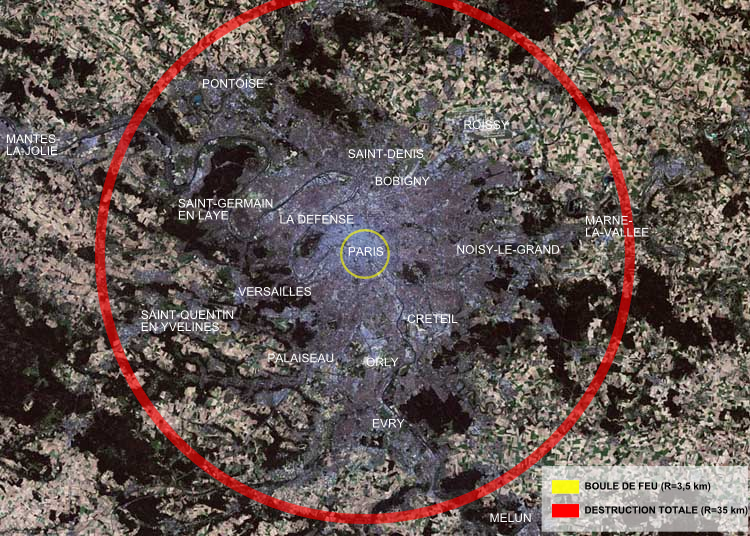
However, in modern Russian society, the idea of creating such weapons is gaining popularity. Like, throw the "Tsar Bomb" on Washington - and Russia's problems will disappear. Who knows what such logic might lead in the future. I hope that the "mind is not enough."
Which corresponds to a mass defect of 2.65 kg.
The development team included A. D. Sakharov, V. B. Adamsky, Yu. N. Babaev, Yu. N. Smirnov, Yu. A. Trutnev, and others.
Encyclopedic YouTube
-
1 / 5
It is worth noting that the above information about the date of commencement of work is in partial contradiction with the official history of the institute (now it is the Russian Federal Nuclear Center - / RFNC-VNIITF). According to her, the order to create a corresponding scientific research institute in the system of the USSR Ministry of Medium Machine Building was signed only on April 5, and work began at Scientific Research Institute-1011 several months later. But in any case, only the final stage of the development of AN602 (already in KB-11 in the summer and autumn of the city (and not the entire project as a whole!) Really took 112 days. Nevertheless, the AN602 was not just the renamed PH202. In the design of the bomb A number of design changes were made - as a result, for example, its centering changed noticeably. The AN602 had a three-stage design: the nuclear charge of the first stage (the calculated contribution to the explosion power - 1.5 megatons) triggered the thermonuclear reaction in the second step (the contribution to the power of the explosion - 50 megatons), and she, in her the sequence initiated the nuclear “Jekyll-Hyde reaction” (nuclear fission in uranium-238 blocks under the action of fast neutrons produced by the fusion reaction) in the third stage (another 50 megatons of power), so that the total calculated power of AN602 was 101.5 megatons.
The original version of the bomb was rejected due to the extremely high level of radioactive contamination that it was supposed to cause - it was decided not to use the “Jekyll-Hyde reaction” in the third bomb stage and replace the uranium components with their lead equivalent. This reduced the estimated total power of the explosion by almost half (to 51.5 megatons).
The first studies on the “theme 242” began immediately after the negotiations of I. V. Kurchatov with A. N. Tupolev (held in the fall of 1954), who appointed A. V. Nadashkevich as his deputy for weapons systems as head of the topic. Conducted strength analysis showed that the suspension of such a large concentrated load will require serious changes in the power circuit of the original aircraft, in the design of the bomb bay and in the suspension and discharge devices. In the first half of 1955 a dimensional and weight drawing of AN602 was agreed, as well as an arrangement drawing of its placement. As expected, the mass of the bomb was 15% of the take-off mass of the carrier, but its dimensions required the removal of the fuselage fuel tanks. Designed for the AN602 suspension, the new beam holder BD7-95-242 (BD-242) was close in design to the BD-206, but significantly load-bearing. He had three bomber locks Der5-6 with a carrying capacity of 9 tons each. BD-242 was attached directly to the power longitudinal beams, edging the bomb bay. We also successfully solved the problem of controlling the discharge of a bomb - electric automation provided only the synchronous opening of all three locks (the need for this was dictated by the security conditions).
On March 12, 1956, a draft resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR on the preparation and testing of product 202 was adopted:
Adopt a draft resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR on the preparation and conduct of testing of the product 202. Include in the draft resolution paragraphs requiring:
a) the Ministry of Medium Machine Building (t. Zavenyagin) and the Ministry of Defense of the USSR (t. Zhukov) at the end of the preparatory work for testing the product 202 report to the CPSU Central Committee on the situation;
b) the Ministry of Medium Machine Building (t. Zavenyagin) to work out the question of introducing into the design of the product 202 a special protection level ensuring the failure of the product when the parachute system fails, and to submit proposals to the CPSU Central Committee.
Instruct tt. Vannikov and Kurchatov final wording of the text of this decision.
Tests
The carrier of the "superbomb" was created, but its real trials were postponed for political reasons: Khrushchev was going to the United States, and there was a pause in the Cold War. The Tu-95V was transferred to the airfield in Uzin, where it was used as a training aircraft and was no longer listed as a combat vehicle. However, in the city, with the beginning of a new round of the Cold War, the tests of the "superbomb" again became relevant. The Tu-95V urgently replaced all the connectors in the electrical system of the discharge and removed the bombshell casements — the actual mass of the bomb (26.5 tons, including the weight of the parachute system — 0.8 tons) and dimensions were slightly larger than the layout (in particular, now its vertical dimension exceeded the size of the bomb bay in height). The plane was also covered with a special white reflective paint.
Khrushchev announced the upcoming tests of the 50-megaton bomb in his report on October 17, 1961 at the XXII Congress of the CPSU.
Tests of the bomb took place on October 30, 1961. Prepared by the Tu-95B with a real bomb on board, manned by a crew consisting of: ship commander A.E. Durnovtsev, navigator I.N. Tick, flight engineer V.Ya. Brui, departed from Olenya airfield and headed for New Earth. In the tests also participated the aircraft laboratory Tu-16A.
Two hours after departure, the bomb was dropped from a height of 10,500 meters on a parachute system for a conventional purpose within the dry nose nuclear test site ( 73 ° 51 ′ s. sh. 54 ° 30 ′ c. d. HGIO). The bomb dropped by parachute area of 1600 square meters. m, with a total weight of 800 kg. The bomb was detonated barometrically at 11 hours and 33 minutes, 188 seconds after the discharge at an altitude of 4200 m above sea level (4000 m above the target) (however, there are other data on the height of the explosion - in particular, the numbers 3700 m above the target were called (3900 m above sea level) and 4500 m). The carrier aircraft managed to fly a distance of 39 kilometers, and the laboratory aircraft - at 53.5 kilometers. The carrier aircraft was dropped by the shock wave at the peak and lost 800 m in height until control was restored. The power of the explosion significantly exceeded the calculated one (51.5 megatons) and ranged from 57 to 58.6 megatons in TNT equivalent. There is also information that according to the initial data, the explosion power of AN602 was significantly overestimated and was estimated to be up to 75 megatons.
In the laboratory, the action of the shock wave from the explosion was felt in the form of a light shaking, without affecting the flight mode of the aircraft. .
Test results
Rumors and hoaxes related to AN602
The test results AN602 were the subject of a number of other rumors and hoaxes. So, sometimes it was claimed that the power of a bomb explosion reached 120 megatons. This was probably due to the “superposition” of information about the excess of the actual power of the explosion over the calculated one by about 20% (in fact, by 14-17%) to the original design capacity of the bomb (100 megatons, more precisely - 101.5 megatons). The newspaper “Pravda” added fuel to the fire of such rumors, in the pages of which it was officially announced that “She<АН602> - yesterday atomic weapons. Now even more powerful charges have been created. ” In fact, more powerful thermonuclear munitions - for example, a warhead for the UR-500 ICBM (GRAU 8K82 index; the known Proton launch vehicle is a modification of it), with a capacity of 150 megatons, although they were actually developed, they remained on the drawing boards.
At various times, rumors were also circulating that the power of the bomb was 2 times lower than planned, as scientists feared the occurrence self-sustaining thermonuclear reaction in the atmosphere. Interestingly, similar concerns (only about the possibility of a nuclear fission reaction occurring in the atmosphere) have already been expressed earlier - in preparation for testing the first atomic bomb to initiate a thermonuclear reaction in seawater
On October 30, 1961, successful tests of the 57-megaton Soviet thermonuclear bomb AN606 passed at the Novaya Zemlya test site. This power is 10 times the total capacity of all the ammunition that was used during the Second World War. AN606 is the most destructive weapon in the history of mankind.
A place
Nuclear testing in the Soviet Union began in 1949 at the Semipalatinsk test site located in Kazakhstan. Its area was 18,500 square meters. km He was removed from the places of permanent residence of people. But not enough to test the most powerful weapon on it. Therefore, in the Kazakh steppe, nuclear charges of low and medium power were blown up. They were necessary to debug nuclear technologies, to study the influence of damaging factors on equipment and facilities. That is, it was, above all, scientific and technical tests.
But in the conditions of military competition, such tests were also needed in which emphasis was placed on their political component, on the demonstration of the crushing power of the Soviet bomb.
There was also the Totsky range in the Orenburg region. But he was less than Semipalatinsk. And besides, it was located in even more dangerous proximity to cities and villages.
In 1954, they found a place where they could test ultra-large-capacity nuclear weapons.
This place was the archipelago of New Earth. He fully met the requirements for the site, which was to test a super-bomb. It was as far as possible from large settlements and communications, and after its closure it should have had a minimal impact on the subsequent economic activity of the region. Also required to conduct a study of the impact of a nuclear explosion on ships and submarines.
The New Earth Islands best met these and other requirements. Their area was more than four times the Semipalatinsk test site and was 85 thousand square meters. km., which is approximately equal to the area of the Netherlands.
The problem of the population that could be affected by the explosions was decided radically: 298 indigenous Nenets were evicted from the archipelago, providing them with housing in Arkhangelsk, as well as in the village of Amderma and on the island of Kolguyev. At the same time, the immigrants were employed, and the elderly were given a pension, despite the fact that they did not have any seniority.
They were replaced by builders.
The nuclear test site on Novaya Zemlya is by no means a clean field onto which bombers drop their deadly cargo, but a whole complex of complex engineering structures and administrative and economic services. These include experimental, scientific and engineering services, energy and water supply services, a fighter aviation regiment, a transport aviation detachment, a division of ships and special-purpose ships, an emergency rescue detachment, a communications center, rear support units, and living quarters.
Three test sites were created at the test site: Black Lip, Matochkin Shar and Sukhoi Nos.
In the summer of 1954, 10 construction battalions were delivered to the archipelago, which began to build the first site, the Black Lip. The builders spent the Arctic winter in canvas tents, preparing the Lip for the underwater explosion scheduled for September 1955 - the first in the USSR.
Product
The development of the Tsar Bomb, which received the AN602 index, was launched simultaneously with the construction of the landfill on Novaya Zemlya - in 1955. And it ended with the creation of a bomb ready for testing in September 1961, that is, a month before the explosion.
Development began at the Scientific Research Institute-1011 of Minsredmash (now the All-Russian Scientific Research Institute of Technical Physics, VNIITF), which was located in Snezhinsk, Chelyabinsk Region. Actually, the institute was founded on May 5, 1955, primarily for the implementation of a grand thermonuclear project. And then his activities spread to the creation of 70 percent of all Soviet nuclear bombs, missiles and torpedoes.
NII-1011 was headed by Kirill Shchelkin, Scientific Director of the Institute, Corresponding Member of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Shchelkin together with a group of luminous nuclear engineers took part in the creation and testing of the first atomic bomb RDS-1. It was he who in 1949 was the last to leave the tower with the charge installed in it, sealed the entrance and pressed the Start button.
Work on the creation of the AN602 bomb, to which the leading physicists of the country, including Kurchatov and Sakharov, were connected, was carried out without any particular complications. But the unique power of the bomb required huge amounts of computation and design work. As well as conducting experiments with smaller charges at the test site - first Semipalatinsk, and then on Novaya Zemlya.
The initial project envisioned the creation of a bomb that would surely break the glass, if not in Moscow, but probably in Murmansk and Arkhangelsk, and even in northern Finland. Since the power was planned in excess of 100 megatons.
The initial scheme of the bomb was three-link. At first, a 1.5 Mt plutonium charge was triggered. He set fire to a fusion reaction, the power of which was 50 Mt. The fast neutrons released as a result of the thermonuclear reaction triggered the nuclear fission reaction in the uranium-238 blocks. The contribution of this reaction to the "common cause" was 50 Mt.
Such a scheme led to an extremely high level of radioactive contamination in the vast territory. And it was not necessary to speak about the “minimal impact of the landfill on the subsequent economic activity of the region after its closure”. Therefore, it was decided to abandon the final phase - the fission of uranium. But at the same time, the actual power of the resulting bomb turned out to be slightly more than was assumed from the calculations. Instead of 51.5 Mt on October 30, 1961, 57 Mt exploded on Novaya Zemlya.
The creation of the AN602 bomb was completed no longer in Snezhinsk, but in the famous KB-11, located in Arzamas-16. The final revision took 112 days.
The result is a monster weighing 26,500 kg, a length of 800 cm and a maximum diameter of 210 cm.
The dimensions and weight of the bomb were already determined in 1955. In order to raise it into the air, we had to significantly upgrade the largest Tu-95 bomber at that time. And this, too, was not an easy job, since the standard Tu-95 could not lift the Tsar Bomb, with a plane weight of 84 tons, it could take only 11 tons of combat load. The share of fuel was 90 tons. In addition, the bomb did not fit in the bomb bay. So I had to remove the fuselage fuel tanks. And also to replace the beam holders of the bomb with more powerful ones.
Work on the modernization of the bomber, called Tu-95 V and made in a single copy, took place from 1956 to 1958. Flight testing continued for another year, during which a technique for dropping a model of a bomb of the same weight and dimensions was being worked out. In 1959, the aircraft was found to be fully satisfying its requirements.
Result
The main result, as it was intended, the political one, exceeded all expectations. The thundering explosion of a previously unknown force made a very strong impression on the leaders of Western countries. He forced to take a more serious look at the possibilities of the Soviet military-industrial complex and somewhat reduce its militaristic ambitions.
The events of October 30, 1961 developed as follows. Early in the morning, two bomber climbed from a remote airfield - the Tu-95 V with the AH602 product on board and the Tu-16 with research equipment and cinematographic equipment.
At 11 hours and 32 minutes from a height of 10,500 meters, the commander of the Tu-95. Major Andrei Egorovich Durnovtsev dropped the bomb. The Major returned to the airfield as a lieutenant colonel and Hero of the Soviet Union.
The bomb, dropping by parachute to the level of 3,700 meters, exploded. At this point, the aircraft managed to get from the epicenter to 39 kilometers.
The test leaders — the Minister of Medium Machine Engineering, EP Slavsky and the Commander-in-Chief of the Missile Forces, Marshal KS Moskalenko — at the time of the explosion were on board the IL-14 at a distance of more than 500 kilometers. Despite the cloudy weather, they saw a bright flash. At the same time, the plane shook the shock wave distinctly. The Minister and Marshal immediately sent a telegram to Khrushchev.
One of the groups of researchers from a distance of 270 kilometers from the explosion point saw not only a bright flash through protective dark glasses, but even felt the impact of a light pulse. In an abandoned village - 400 kilometers from the epicenter - wooden houses were demolished, and stone houses were deprived of roofs, windows and doors.
Mushroom from the explosion reached a height of 68 kilometers. In this case, the shock wave, reflected from the ground, prevented the plasma ball from descending to the earth, which would incinerate everything in a vast space.
A variety of effects were monstrous. A seismic wave circled the globe three times. Light radiation was able to cause third-degree burns at a distance of 100 km. The roar from the explosion was heard in a radius of 800 km. Due to the ionizing effects, radio interference in Europe has been observed for more than an hour. For the same reason, communication with the two bombers was gone for 30 minutes.
At the same time, the test turned out to be surprisingly clear. Radioactive radiation within a radius of three kilometers from the epicenter two hours after the explosion was only 1 milli-raygen per hour.
The Tu-95 V, despite the fact that it was located 39 kilometers from the epicenter, dropped by a shock wave at its peak. And the pilot was able to regain control of the aircraft, only having lost 800 meters in height. The bomber completely, including screws, was painted with white reflective paint. But when examining it, it was found that the paint had fragmentary burned out. And some elements of the design even melted and deformed.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the 100-megaton filling could fit in the case of AN602.




